Estimated reading time: 20 minutes
If you’ve ever stared at an empty prompt box wondering what to type, and then watched your AI tool spit out something that felt completely off, you’re not alone. I’ve been there too. It is one of the most frustrating feelings, especially when you know what you want but the output just doesn’t match. That is exactly why learning how to write better AI prompts makes such a difference, turning vague instructions into results that actually align with your goals.
The truth is, AI doesn’t magically “get it.” It needs guidance. Good prompts aren’t about clever wording or technical tricks. They are about clarity, intent, and structure. Whether you’re a new writer exploring ChatGPT, a solopreneur writing client emails faster, or a small agency building reusable templates for your team, learning how to write better AI prompts can save time, reduce edits, and help you focus on the human side of your work.
Over the past year, I’ve tested hundreds of prompts across various tools, including ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini. I’ve used them for blog drafts, outreach emails, and content briefs. And what I’ve learned is simple: how to write better AI prompts is not a mystery, it is a skill. One that anyone can learn with the right examples and a clear framework.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through that framework. From basic concepts to advanced techniques, I’ll share the actual strategies I use every day. I’ll also show you common mistakes, give you copy-ready examples, and link to trusted resources I recommend through platforms like EdgeScribe.
First, let’s break down what an AI prompt is and why it matters more than ever in 2025.
What Are AI Prompts and Why Do They Matter?
If you’ve ever typed a request into ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini, whether it is “write me a blog outline” or “explain SEO like I’m five,” you’ve already used an AI prompt. An AI prompt is a text instruction that tells artificial intelligence models (like ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini) exactly what task to perform and how to respond. These AI models use sophisticated algorithms to interpret your prompt and generate a response.
But here’s the thing: research shows that nearly half of the performance gains from advanced AI models actually come from how users adapt their prompts, not just from the model itself. The quality of your prompt directly shapes the quality of the AI’s output. If you want consistent, accurate results, you need to understand how to write better AI prompts that give the model clear direction.
A vague or incomplete prompt leaves too much room for guesswork, which means you spend more time rephrasing and refining. However, a strong, well-structured prompt can significantly boost efficiency, helping the AI deliver relevant, accurate, and usable results in fewer iterations.
Why do prompts matter more than you think?
For writers, solopreneurs, and small agencies, learning to craft great prompts isn’t just about saving time; it’s about maintaining control over tone, accuracy, and brand alignment in an AI-driven workflow.
- AI is only as good as your input: Garbage in, garbage out still applies. A great tool can still produce mediocre content if you feed it unclear instructions.
- They bridge the gap between human creativity and machine efficiency: Prompts let you steer AI towards your unique voice, perspective, and goals instead of sounding like generic internet text.
- Well-crafted prompts cut editing time: The better the first draft, the less rework you need, freeing you to focus on strategy and final polish.
- They’re a competitive advantage: In a world where anyone can access AI, those who know how to guide it produce faster, better, and more original content.
- They future-proof your skill set: As AI tools evolve, prompt literacy will remain a core skill for quality control and creative direction
Prompt Quality → Performance (quick comparison)
In short: AI prompts are the new briefs. Just like a vague client brief produces an unfocused piece of work, a vague AI prompt delivers generic results. The more precise and thoughtful your prompt, the more value you get from AI and the more your content stands out in a sea of sameness.
How Do AI Models Process and Interpret Prompts?
If you’ve ever typed something into ChatGPT or another AI tool and thought, “How did it know exactly what I meant?”, you’re not alone. For new writers, solopreneurs, and even small agency teams, the idea of “AI understanding” can feel a little like magic, except it is not magic at all. It is a systematic, step-by-step process that is surprisingly logical once you break it down.
Here’s the core idea: AI doesn’t truly “understand” in a human sense. Instead, it follows a sequence powered by natural language processing (NLP) to take your prompt, break it into meaningful parts, match patterns from its training data, and generate a response that aligns with what it predicts you need.
From my own experience teaching beginners and working with busy business owners, the real challenge isn’t in knowing that AI can respond. The real challenge is understanding how it processes your input so you can learn how to write better AI prompts that work for you instead of against you.
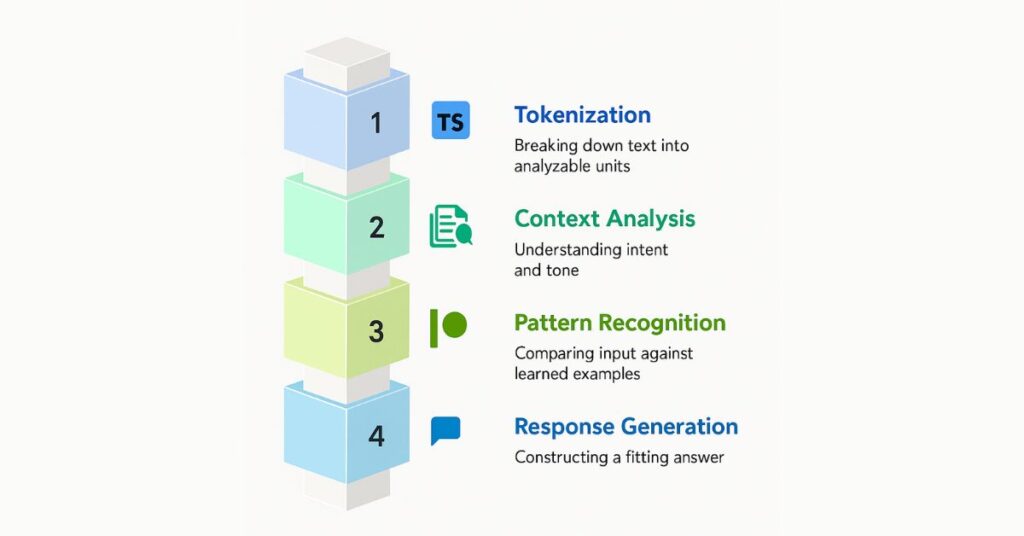
The 4-Step AI Processing Method
To truly understand how to write better AI prompts, it helps to know what happens inside the model once you hit “enter.” AI doesn’t interpret your request like a human would. Instead, it follows a logical sequence that breaks your text into parts, analyzes context, matches patterns from its training data, and then generates a response.
This process is often invisible to users, but once you see how it works, you can shape your prompts more effectively and guide the AI toward accurate, high-quality outputs. The 4-Step AI Processing Method:
- Tokenization: Your text is split into tiny, analyzable units called tokens. Think of it like breaking a paragraph into Lego bricks.
- Context Analysis: The AI looks at the surrounding “bricks” to understand intent, background, and tone.
- Pattern Recognition: It compares your input against billions of learned examples from training data.
- Response Generation: It predicts and constructs an answer that fits both your words and the patterns it knows.
Tokenization: Breaking Your Prompt Into Lego Bricks
Before an AI can respond, it first chops your text into small units called tokens.
- A token can be a single letter, part of a word, or a whole word, depending on the language and model.
- Think of your prompt as a Lego castle: tokenization is taking it apart into individual bricks so the AI can work with them.
Why It Matters to You:
If your prompt is messy, unclear, or jumbled, tokenization will still break it into parts, but the AI might not link them in the way you expect. Clearer word choices = better “bricks” to build your answer.
Practical Tip: Use straightforward language and avoid cramming multiple unrelated requests into one sentence.
| Instead of:“Give me SEO advice, a blog title, and rewrite my intro”Do this:“Step 1: Give me SEO advice for beginners. Step 2: Suggest 5 blog titles. Step 3: Rewrite my intro for clarity.” |
Context Analysis: Figuring Out What You Really Mean
Once your prompt is tokenized, the AI starts looking at the relationships between your tokens.
- This is like reading a sentence and noticing that “bank” in “river bank” means something different than “bank” in “savings bank.”
- The AI uses a context window (a limited number of tokens it can “see” at one time) to understand tone, background, and your likely intent.
Why It Matters to You:
If you don’t give enough context, the AI will guess—and its guess might not match your vision.
Practical Tip: Always front-load essential details:
| Bad prompt:“Write a blog intro.” Better prompt: “Write a friendly, engaging blog intro for beginner solopreneurs about how to save time with AI tools, in under 100 words.” |
Pattern Recognition: Matching Your Request to Its Knowledge Base
Now the AI checks your prompt against patterns it learned during training.
- It doesn’t “search the internet” in real time. Instead, it draws on a massive library of examples it has seen before.
- If your request matches a known pattern, it predicts what words and structures should logically come next.
Why It Matters to You:
If your prompt is vague, the AI may latch onto the wrong pattern. For example, “write about apple” could produce tech content (Apple Inc.) or fruit content (apple pie recipes).
Practical Tip: Be specific enough to lock onto the right pattern.
| Instead of:“Write about an apple.”Do this:“Write a playful blog post for health-conscious parents about the nutritional benefits of apples.” |
Response Generation: Building the Answer Block by Block
Finally, the AI assembles its prediction into a coherent response.
- It decides on the next most likely token over and over until your answer is complete.
- Each choice depends on the tokens that came before it, which is why your initial instructions matter so much.
Why It Matters to You:
If you set the wrong tone or structure in your prompt, the AI will faithfully carry that through the entire answer, even if it’s not what you wanted.
Practical Tip: Use role and style instructions at the start to guide the whole output.
| Example:“You are an experienced SEO coach. Write a step-by-step blog section in a friendly, conversational tone.” |
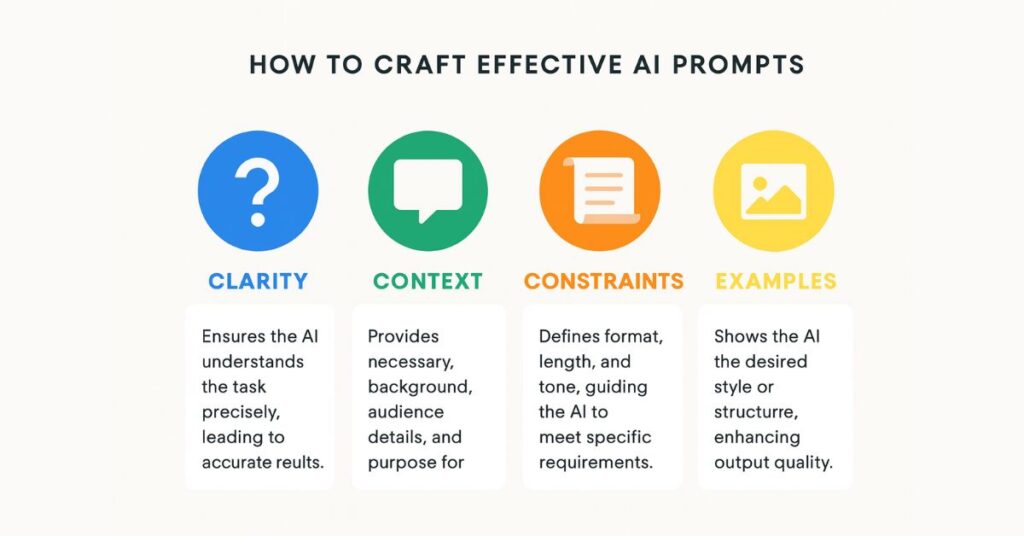
What Are the Core Components of Excellent AI Prompts?
A great AI prompt isn’t just good wording — it’s a small piece of strategy. Whether you’re a new writer figuring out ChatGPT for the first time, a solopreneur using AI to scale content, or a small agency building repeatable systems, the difference between a mediocre output and one that feels spot-on comes down to how well you design your prompt.
I’ve tested thousands of prompts in real-world client work, training workshops, and my writing projects. I’ve learned that winging it with AI wastes time, but having a proven structure can turn AI from a guesswork tool into a reliable creative partner. In fact, real-world cases demonstrate that well-structured prompts can reduce the need for follow-up queries by about 20 percent, helping teams get better outputs on the first try. One of the most effective structures I use (and teach) is the CLEAR Framework.
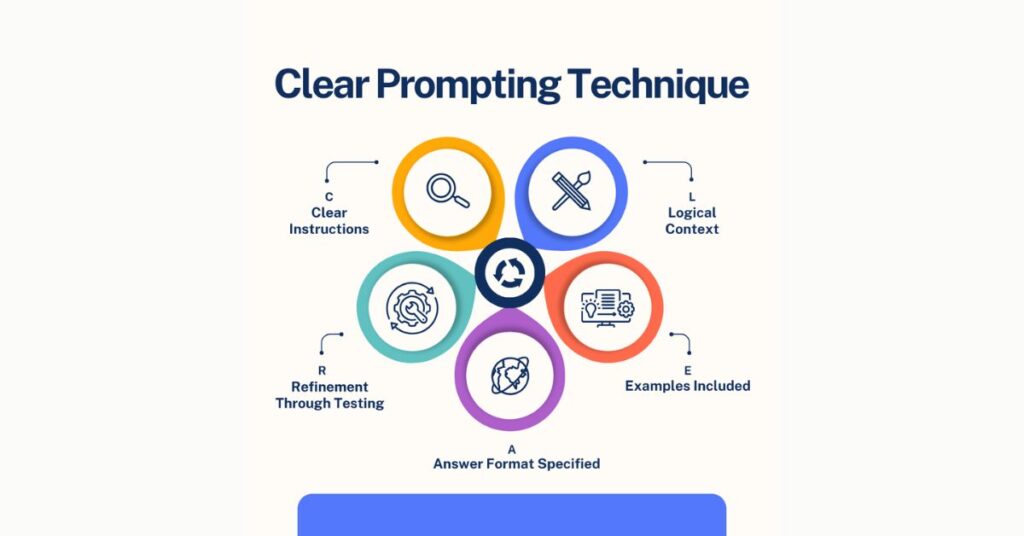
What is the CLEAR Framework for AI Prompts?
Think of a good AI prompt like a well-packed travel bag. Everything you need is in there, neatly arranged, and nothing important is left behind. The CLEAR framework is that packing list for your prompt, making sure every single “must-have” is covered before you send it off to the AI.
CLEAR stands for:
- Clear instructions
- Logical context
- Examples included
- Answer format specified
- Refinement through testing
| Component | Description | Example |
| Clear | Specific, unambiguous instructions | “Write a 300-word blog intro on beginner SEO tips.” |
| Logical | Relevant background context | “For a B2B SaaS targeting SMEs in the HR tech space.” |
| Examples | Show desired style or format | “Like this: [sample text].” |
| Answer | Define output structure | “As 3 numbered points with subheadings.” |
| Refinement | Test and improve prompts | “If too formal, add: use conversational tone.” |
Pro tip from experience:
When I first started teaching AI prompting to small agency teams, the biggest lightbulb moment came from the “Examples” step. Once writers saw a concrete sample, their AI outputs instantly matched the desired tone — no extra rounds of feedback.
What Essential Elements Should Every AI Prompt Include?
If the CLEAR framework is your packing list, these elements are the actual items you’re putting into the bag. Without them, your prompt might still “work” — but it won’t work well.
- Role Definition — “Act as a [specific expert role].”
- Task Specification — A clear action verb + a specific objective.
- Context Provision — Include background info and any constraints.
- Format Requirements — Specify output structure and length.
- Quality Criteria — Define what “good” looks like.
Quick Prompt Template:
| Act as [ROLE] with [EXPERTISE]. Create [DELIVERABLE] for [AUDIENCE] that [OBJECTIVE]. Include [REQUIREMENTS] and format as [STRUCTURE]. Ensure [QUALITY_CRITERIA]. |
Why does it work for different readers?
- New writers get a step-by-step recipe they can copy-paste without worrying about AI jargon.
- Solopreneurs save time by skipping vague prompts and going straight to usable results.
- Small agencies can standardize prompts so their whole team produces consistent work.
When you combine the CLEAR framework with these essential elements, your AI prompts stop being one-off experiments and start becoming repeatable tools you can trust. Next, let’s look at how to actually write prompts that feel human while still being strategically structured.
What Are the Best AI Prompting Techniques for 2025?
Suppose AI prompts are the instructions you give to a digital assistant. In that case, mastering them in 2025 is a bit like learning the perfect coffee order at your favorite café—clear, specific, and tailored to get exactly what you want. I’ve tested dozens of AI writing techniques, some that made my workday smoother, and others that left me wishing I’d just typed it myself.
In this section, I’ll share the prompting strategies I’ve found to be most effective for 2025, including when to go minimalist and when to guide AI with rich context.
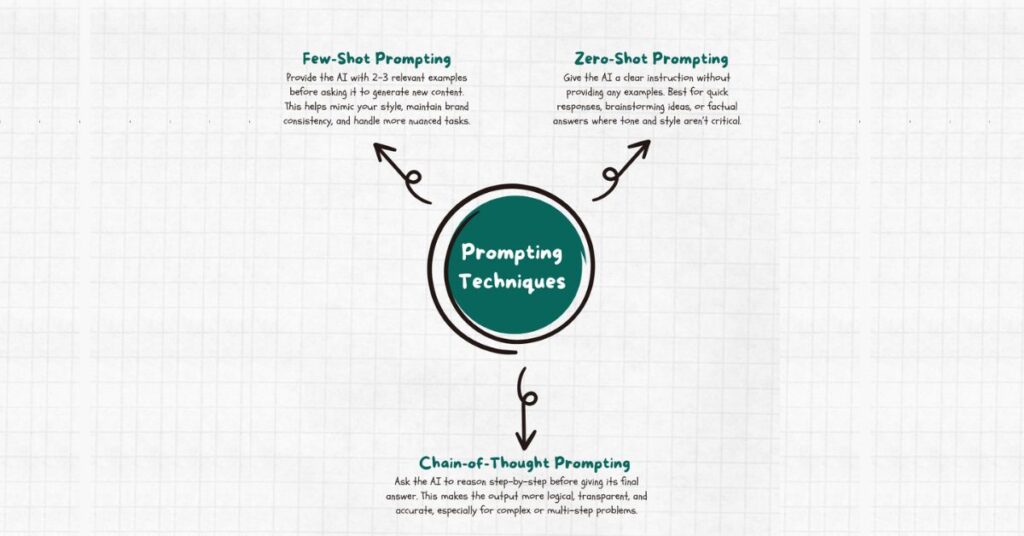
When Should You Use Zero-Shot vs Few-Shot Prompting?
Ever send someone a vague one-liner and then wonder why their reply missed the mark? That’s zero-shot prompting in a nutshell—no examples, just instructions. Sometimes it works brilliantly. Other times, it’s a gamble.
Few-shot prompting, on the other hand, gives AI a couple of examples to “learn” your style before generating new output. Think of it as showing, not just telling.
Here’s how they compare:
| Prompting Style | How It Works | Best For | Watch Out For |
| Zero-Shot | You give AI a clear instruction without any examples. | Quick tasks, factual answers, brainstorming ideas. | Risk of bland or misaligned tone if the task needs nuance. |
| Few-Shot | You provide AI with 2–3 relevant examples before asking it to generate something new. | Mimicking your style, creating consistent brand voice, nuanced tasks. | Takes longer to set up; bad examples lead to bad output. |
Pro Tip: If you’re in a rush or need raw ideas, start zero-shot. If tone, accuracy, and brand feel matter, invest the extra minute in a few-shot.
How Does Chain-of-Thought Prompting Improve Results?
Imagine asking a chef for the perfect cake recipe. One chef just hands you a cake—looks fine, but you have no idea what went into it. The other walks you through each step, from whisking the eggs to checking if the sponge is springy. Which one are you more likely to trust?
That’s exactly what Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting does for AI. It makes the model “show its work.” By breaking a problem into smaller reasoning steps, AI becomes more accurate, often improving results by up to 40% for complex tasks.
What Is Chain-of-Thought Prompting?
CoT prompting explicitly asks AI to reason step-by-step before giving the final answer. This makes the output more logical, transparent, and less prone to wild guesses.
How to Implement It:
- Add “Let’s think step by step” to your prompt.
- Request intermediate reasoning before the answer.
- Ask for a conclusion supported by that reasoning.
- Specify the exact format for the final answer.
Detailed Example — Blog Topic Selection
| Prompt:I need a blog post idea for a small business marketing audience that will rank in search within 3 months. Let’s think step by step. AI’s Chain-of-Thought Response: Step 1 – Understand the audience: Small business owners looking for quick, budget-friendly marketing wins. Step 2 – Define constraints: Needs to have low-to-medium keyword difficulty, high search intent, and evergreen potential. Step 3 – Keyword research reasoning: Identify topics under 40 KD (keyword difficulty) with 500–2000 monthly searches. Step 4 – Shortlist ideas:“Free tools for small business marketing”“Beginner’s guide to local SEO”“How to repurpose content for more reach” Step 5 – Compare options:Free tools → competitive but high CTR potentialLocal SEO → relevant, moderate KD, strong ROIContent repurposing → low KD, easy to execute, high value for the audience Step 6 – Choose best fit: “How to Repurpose Your Content to Get 3X More Reach” → Low competition, relevant, actionable, likely to attract backlinks. Step 7 – Conclusion: Final topic: “How to Repurpose Your Content to Get 3X More Reach”, with subtopics on social media, blog-to-video, and email marketing reuse. |
Let’s understand it from a mathematical example.
Detailed Example — Train Problem
| Prompt:If a train leaves New York at 3 PM going 60 mph toward Boston, and another leaves Boston at 4 PM going 75 mph toward New York, when will they meet? Let’s think step by step. AI’s Chain-of-Thought Response: Step 1 – Define known data: Distance between New York and Boston = 215 miles. Train A speed = 60 mph, Train B speed = 75 mph. Train A leaves 1 hour earlier. Step 2 – Calculate Train A’s head start: In the first hour, Train A travels 60 miles. Step 3 – Remaining distance after head start: 215 – 60 = 155 miles. Step 4 – Combined speed once both trains are moving: 60 + 75 = 135 mph. Step 5 – Time needed to cover the remaining 155 miles: 155 ÷ 135 ≈ 1.15 hours (~1 hour 9 minutes). Step 6 – Add this to Train B’s departure time: 4:00 PM + 1 hour 9 minutes = 5:09 PM. Step 7 – Conclusion: The two trains meet at 5:09 PM, about 2 hours and 9 minutes after Train A departs. |
Pro Tip: CoT is gold for complex decision-making. Think budget breakdowns, multi-step content strategies, troubleshooting code errors, or legal contract reviews.
What Are the Most Common AI Prompting Mistakes and How Do You Avoid Them?
When you first start working with AI writing tools, it’s tempting to think, “If I just type in what I need, it’ll figure it out.” But much like giving a freelancer vague instructions and hoping for magic, AI only works as well as the prompts you feed it.

I’ve seen the same prompting mistakes drain hours of productivity and deliver results that feel off. The good news is that most of these errors aren’t technical. They are about clarity, context, and structure. If you can learn how to write better AI prompts and avoid the eight most common missteps, you’ll see your AI output improve in accuracy, tone, and usefulness almost immediately. Let’s start by breaking down exactly which mistakes hurt prompt performance the most and how to avoid falling into them.
What Critical Errors Ruin AI Prompt Effectiveness?
Think of AI like a sharp kitchen knife—powerful, versatile, but only as good as your technique. Most disappointing AI outputs don’t come from the model “not being smart enough” but from prompts that unintentionally set it up to fail. After reviewing hundreds of real-world prompts from content creators and marketers, these are the most common pitfalls—and exactly how to sidestep them.
The Top Prompting Mistakes (and How to Fix Them):
- Being Too Vague
- The Mistake: Writing prompts that lack detail, e.g., “Write an article about marketing.”
- Why It Hurts: AI guesses what you want, often missing tone, structure, or audience intent.
- The Fix: Add specifics—audience, style, format, length, and purpose.
- Example Before: “Write about email marketing.”
- Example After: “Write a 600-word beginner’s guide to email marketing for small business owners, using a friendly, conversational tone and including 3 actionable tips.”
- Skipping Context
- The Mistake: Not giving AI enough background on your brand, product, or audience.
- Why It Hurts: Outputs sound generic and disconnected from your voice.
- The Fix: Always include relevant brand and audience context.
- Example Before: “Write a product description for our planner.”
- Example After: “Write a playful yet professional product description for our eco-friendly, refillable leather planner aimed at remote-working creatives.”
- No Output Constraints
- The Mistake: Letting AI decide structure and format entirely.
- Why It Hurts: You get long, rambling responses or missing sections.
- The Fix: Specify structure—number of sections, bullet points, or headings.
- Example Before: “Explain SEO to beginners.”
- Example After: “Explain SEO to beginners in 5 bullet points, each under 40 words, and end with a one-sentence takeaway.”
- Overloading the Prompt
- The Mistake: Stuffing multiple unrelated requests into one prompt.
- Why It Hurts: AI tries to cover everything, producing scattered, unfocused content.
- The Fix: Break complex tasks into smaller, sequential prompts.
- Example Before: “Write a blog about Instagram ads, then make a 10-slide carousel and a TikTok script.”
- Example After: First, ask for the blog, then request repurposing into slides, then into a script.
- Ignoring Role or Perspective
- The Mistake: Not telling AI who it’s supposed to be when writing.
- Why It Hurts: Outputs lack authenticity or authority.
- The Fix: Assign a role that matches the task.
- Example Before: “Explain brand storytelling.”
- Example After: “You are an experienced brand strategist speaking to a group of first-time founders. Explain brand storytelling in under 300 words.”
- Not Iterating
- The Mistake: Accepting the first output without refining the prompt.
- Why It Hurts: You miss out on drastically better results that small tweaks could achieve.
- The Fix: Rerun with clarified instructions, tone adjustments, or added examples.
How to Spot a Weak Prompt Before You Send It
Before you hit “enter,” give your prompt a 10-second health check. This quick scan can save you from vague, bloated, or unfocused outputs that waste time.
The Weak Prompt Checklist:
- Clarity Test:
- Can a stranger understand exactly what you’re asking?
- If the request could mean 3 different things, it’s not ready.
- Context Test:
- Does the AI know who you are, who you’re talking to, and why?
- If not, add brand, audience, and intent details.
- Constraints Test:
- Have you given clear limits on format, length, or structure?
- If not, expect rambling or missing pieces.
- Focus Test:
- Is the prompt tackling only one main task?
- If it’s doing too much, break it into steps.
- Role Test:
- Have you told the AI what role to play? (e.g., journalist, brand strategist, copy editor)
- Without this, tone and authority can feel off.
Example of a Weak Prompt → Strong Prompt:
| Weak:“Write a post about social media.”Strong:“As a social media strategist speaking to solopreneurs with limited budgets, write a 300-word blog post on how to grow Instagram reach organically in 2025. Use 3 numbered tips and a friendly but authoritative tone.” |
Pro Tip:
Before sending a prompt, ask yourself:
If I gave this exact instruction to a human freelancer, would they know exactly what to do?
If not, refine it—your AI will thank you with better results.
Wrapping It All Up: Better Prompts, Better Results
If there’s one takeaway from this guide, it’s that AI isn’t some mystical black box, it’s a responsive collaborator that works best when you speak its language. Whether you’re a new writer just figuring out how to make ChatGPT sound like you, a solopreneur juggling five other things while trying to get content out the door, or a small agency owner training your team, learning how to write better AI prompts is no longer “nice to have.” It is the skill that turns guesswork into consistent, client-ready output.
By focusing on clarity, context, and a structured approach like CLEAR or Chain-of-Thought, you cut down revisions, save hours, and keep your unique voice intact. The better your instructions, the more AI feels like an extension of your thinking, not a replacement for it.If you want ready-to-use prompt frameworks, real-world examples, and step-by-step guides tailored for writers and content creators, you’ll find them waiting for you inside EdgeScribe. Contact us now.


